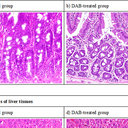
Rutin (quercetin rutinoside) induced protein-energy malnutrition in chronic kidney disease, but quercetin acted beneficially.
Ключови думи
Резюме
Nutraceutically, much of the literature has indicated that an aglycon and its related glycoside would act similarly. However, controversial reports are accumulating. We hypothesize that rutin (RT) and quercetin (QT) pharmacodynamically could act differently. To confirm this, doxorubicin (DR) (8.5 mg/kg) was used to induce rat chronic kidney disease (CKD) and then treated with QT and RT (each 70 mg/kg body weight per day) for 13 weeks. QT exhibited better body weight gaining effect (420 ± 45) vs RT, 350 ± 57 g/rat (p < 0.001). DR raised the ratio kidney-to-body weight (%) to 0.82 (p < 0.001) vs RT, 0.62 (p < 0.01), and QT, 0.35 (p < 0.01). DR reduced the glomerular filtration rate to 25.2 vs RT, 48 ± 11.3; QT, 124.7 ± 12.8 (p < 0.001) and the control, 191.5 ± 15.7 mL/h (p < 0.001). DRCKD reduced hematocrit to 29 ± 5; RT, to 28 ± 5 (p < 0.05); QT, to 36 ± 6 vs the control 37.5 ± 4%, (p < 0.01). DRCKD reduced the serum albumin (s-Ab) to 2.1 ± 0.2 (p < 0.001); QT, to 2.7 ± 0.2 (p < 0.05) vs the normal 4.3 ± 0.5 g/dL, yet RT was totally ineffective. DRCKD raised serum cholesterol level to 340 ± 30; vs RT, 260 ± 12; QT, 220 ± 25; and the normal value, 70 ± 25 mg/dL. DRCKD increased serum triglyceride to 260 ± 15 (p < 0.001), RT and QT restored it to 170 ± 25 and 200 ± 15 (p < 0.05) vs the normal 26-145 mg/dL. DRCKD elevated blood urea nitrogen to 38 ± 3 vs RT, to 98 ± 6 mg/dL (p < 0.001), implicating "protein-energy malnutrition". RT stimulated serum creatinine (sCr) production to reach 6.0 ± 0.9 mg/dL (p < 0.001). QT did not alter the sCr level. RT but not QT induced uremia and hypercreatininemia. DR significantly downregulated Bcl-2, but highly upregulated Bax, Bad, and cleaved caspase-3, implicating the intrinsic mitochondrial pathway. DR damaged DNA, but QT completely rescued such an effect and recovered renal amyloidosis and collagen deposition. Conclusively, RT and QT act differently, and RT is inferior to QT with respect to treating CKD.